

CNT 4704: Computer Communication Networks
Fall 2009
Homework 1
(assigned 09/24; due: 10/01, submitted via webcourse)
1. The
advantage of packet switching vs. circuit switching. The
following figure shows that many users are sharing a 1Mbps access link
to the Internet. Suppose each user is either in active status that
required data access rate of 100kbps, or in silence status that the
user requires no data. Each user is active only 10% of the time ,
and users are independent with each other in their activities.
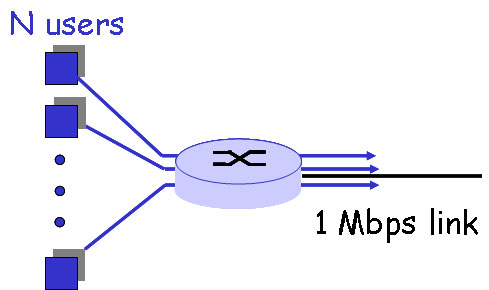
You can leave you answer in terms of an expression (e.g., with sums) to be evaluated (i.e., you need not provide a specific numerical value).
2. Perform "traceroute" from your computer at home to www.google.com at three different hours of the day (If use Windows, please use tracert).
a). Copy the three times traceroute report in your homework report.
b). Find the number of routers in the path at each of the three hours. Did the paths change during any of the hours? Did the traceroute go to different IP addresses of www.google.com?
c). Try to identify the regions or ISP networks that the traceroute packets pass through from the source to the destination.
3. True or false? If a statement is
false, explain briefly why it is wrong:
a). A user requests a Web page that consists
of some text and two images. For this page, the client will send one
request message and receive three response messages.
b). Two distint Web page (e.g.,
www.mit.edu/research.html and www.mit.edu/students.html can be sent
over the same persistent connection.
c). With non persistent connections between
browser and origin server, it is possible for a single TCP segment to
carry two distinct HTTP request messages.
d). The Date: header in the HTTP
response message indicates when the object in the response was last
modified.
4. Suppose you open a startup company "flashNetwork" and want to set up your company network. Your network has the following servers:
Your company's email address is "username@flashNetwork.com".
a). What resource records (RRs) do you need to provide to the upper-level ".com" Registrar?
5.
Consider
the
networks shown in the figure below. Assume computers in the institution
send out 13 requests per second. Each object average size is 100,000
bits. Also assume the internet side delay of a request is 1 seconds.
Using M/M/1 queue to model the access delay in the 1.5Mbps access link.
That is to say, the average delay time for an object on the access link
is E[T] = 1/(x-y), where y is the
arrival rate of objects to the access link and x is the
service rate of the access link (i.e., on average, the access link
could server x objects per second).
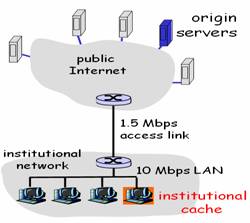
a). Find the total average response time when no institutional cache is used. (Hint: total delay includes Internet delay, access link delay, and LAN delay)
b). Now suppose the institutional cache is used.
The hit rate for the cache is 0.6. Find
the total average response time.